|
Performance of the Arab countries on the Open Budget Survey 2021
Arab Region - Tuesday, May 31, 2022
The International Budget Partnership released the results of its 2021 Open Budget Survey (OBS), which evaluates the level of transparency, oversight and public participation in the budget practices of 120 countries.
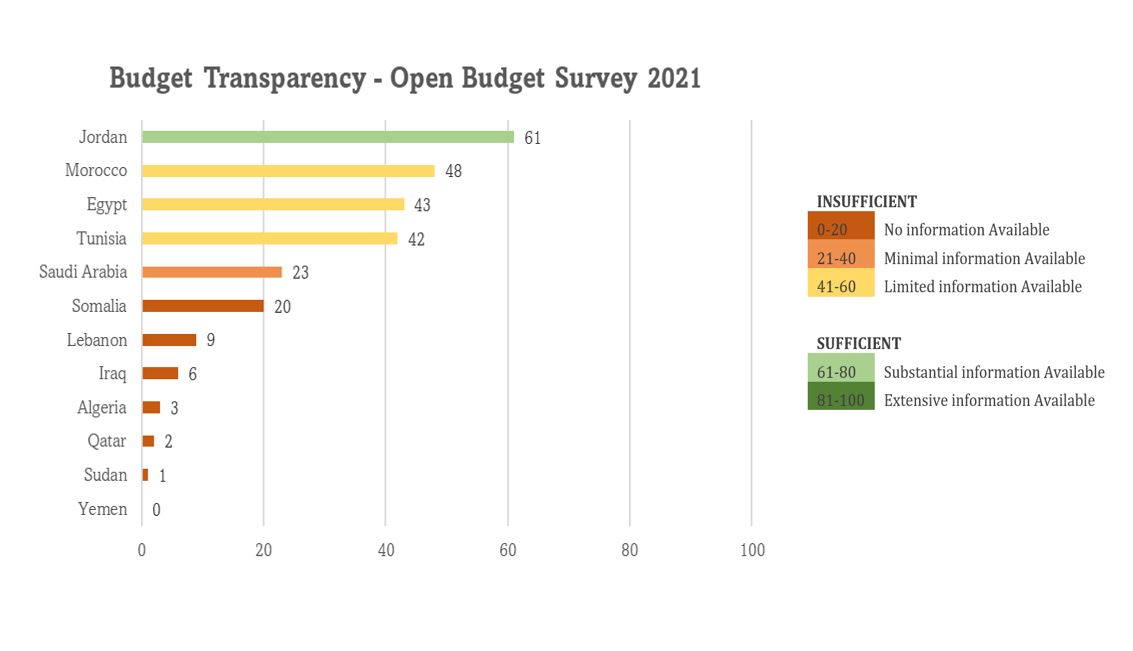
The global average budget transparency level improved by 1 point from 44 to 45 (out of 100) between 2019 and 2021. Georgia ranked first out of 120 countries with a score of 87 (out of 100), while Yemen, Comoros, and Venezuela came in last place on budget transparency with a score of 0 (out of 100). In the Arab states’ region, the regional average improved from 18.5 in 2019 to 21.5 (out of 100) in 2021. Seven out of the twelve Arab countries included in the OBS this year have made progress: Algeria, Qatar, Lebanon, Somalia, Saudi Arabia, and Tunisia. Jordan remains at the top, with a score of 61 (out of 100), and a ranking of 32 out of 120 countries worldwide. A transparency score of 61 (out of 100) or higher indicates a country is publishing sufficient information to support informed public debate.
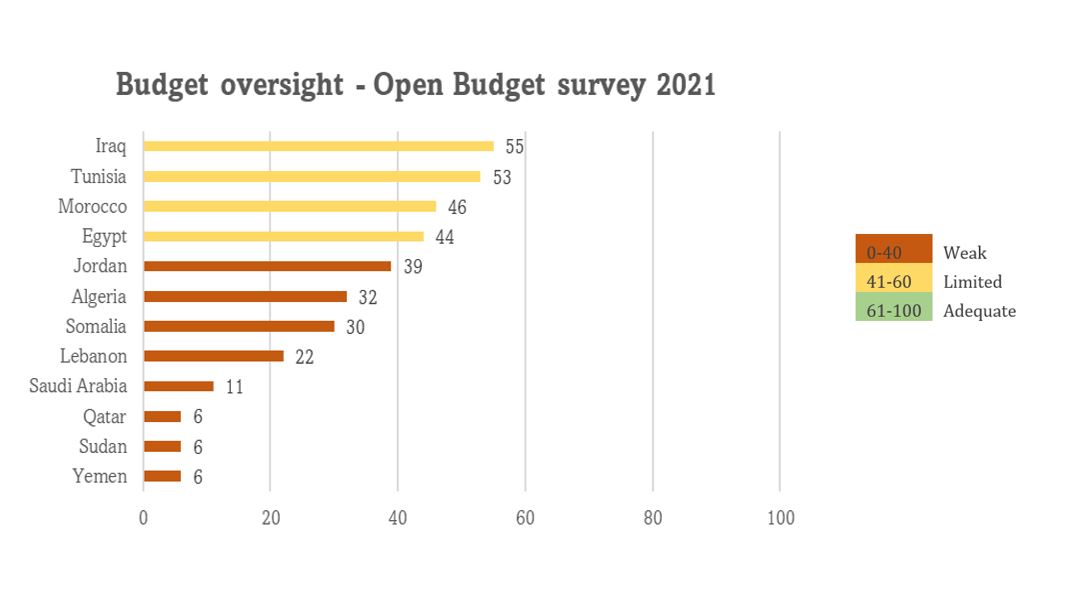
The global average score for budget oversight by formal oversight institutions declined by 1 point from 53 to 52 (out of 100). Germany ranked first out of 120 countries on oversight with a score of 91 (out of 100), while Yemen, Qatar, and Sudan came in last place with a score of 6 (out of 100). In the Arab states’ region, the regional average score slightly regressed from 31 to 29 (out of 100). Four out of the twelve Arab countries included in the OBS have made progress, including Morocco, Tunisia, Somalia, Lebanon, and Iraq, with the latter remaining at the top for the second year in a row at a score of 55 (out of 100).
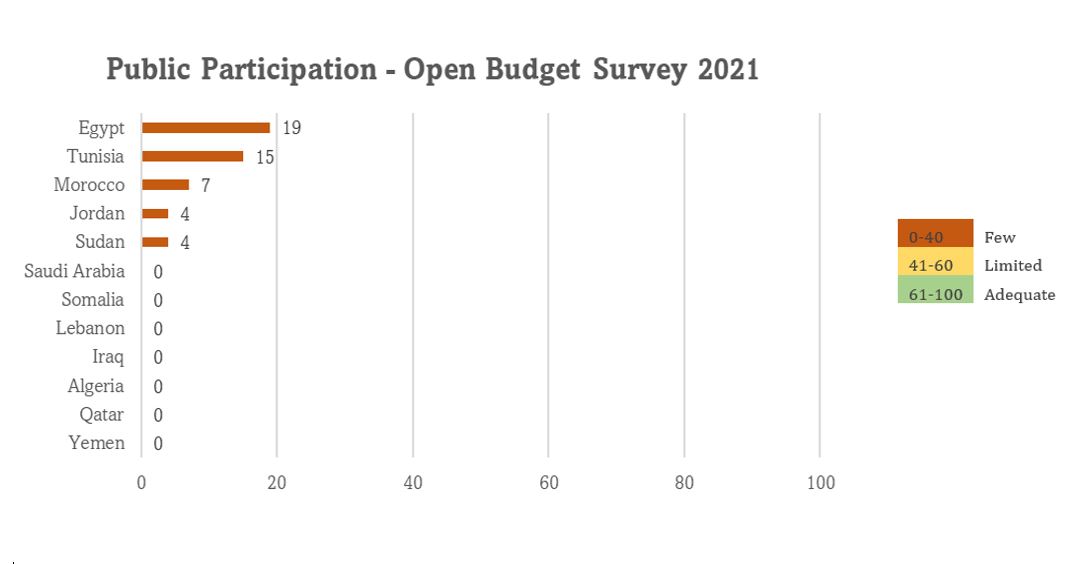
On the public participation assessment of opportunities for the public to participate meaningfully in the budget process, the global average score for public participation was unchanged at 14 (out of 100). South Korea ranked first with a score of 59 (out of 100). In the Arab states’ region, the regional average remains unchanged at a score of around 4 (out of 100) in 2019 and 2021. Two Arab countries, Egypt and Sudan, improved 4 points (out of 100). Seven other Arab countries remain unchanged at a score of 0 (out of 100).
The 2021 Open Budget Survey report suggests that significant, sustained and meaningful progress towards more open budgeting systems is possible. Norms and standards for what constitutes good practice exist; resources and technical assistance to support committed governments are available. According to the report, what is required is a commitment by government to prioritize and substantially advance this agenda.
Detailed country results may be accessed here.
About the Open Budget Survey
The Open Budget Survey (OBS) assesses the three components of a budget accountability system. The first is referred to as Transparency which denotes the budget transparency score (also known as the Open Budget Index). This component measures public availability of eight key budget documents: Pre-Budget Statement, Executive’s Budget Proposal, Enacted Budget, Citizens Budget, In-Year Reports, Mid-Year Review, Year-End Report, and Audit Report. These documents must be published online, in a time-frame consistent with good practices, and must include information that is comprehensive and useful.
The second component is referred to as Public Participation. It assesses how well or to what degree the executive, the legislature, and the supreme audit institution each provides opportunities for the public to engage during different cycles of the budget process.
The third component is known as Budget Oversight, where it examines the role played by formal oversight institutions such as the legislature and the supreme audit institution (or SAI) in the budget process and the extent to which they are able to provide robust oversight of the budget.
|